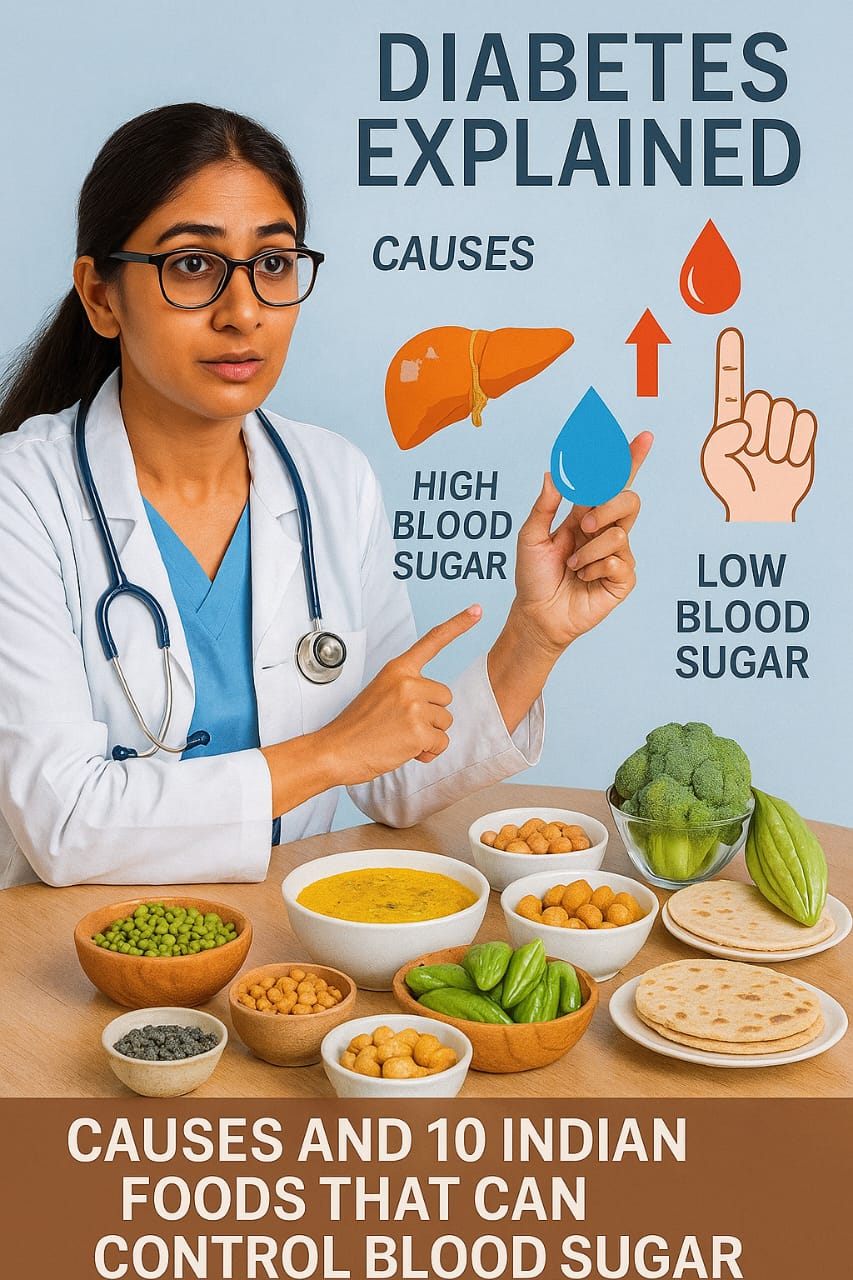
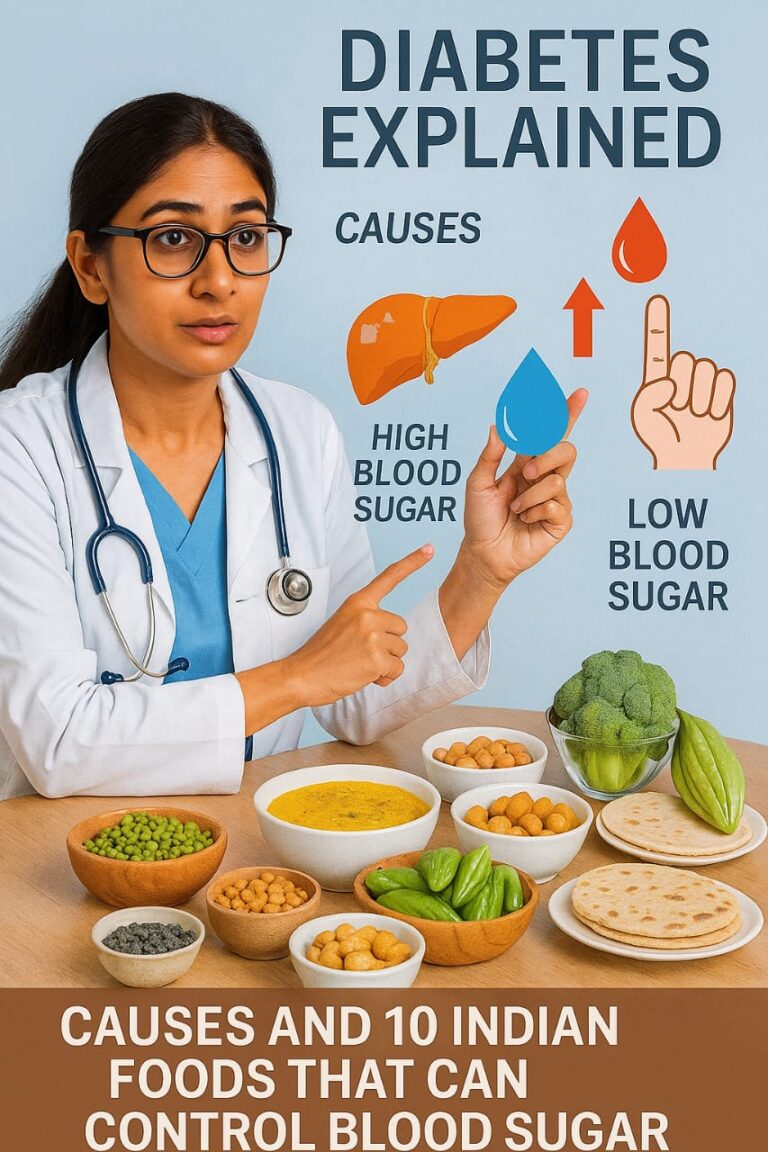
Diabetes is a chronic health condition in which your body is unable to make insulin or produces insufficient insulin, resulting in high blood glucose levels. The global diabetic population is expected to reach an epidemic level in the next few years. Although diabetes can cause a variety of health concerns, frequent medication, exercise, and dietary adjustments can help you manage it.
Are you concerned that you may have high blood sugar levels and develop diabetes? This article will discuss diabetes, its causes, and which Indian foods can control the risk of diabetes.
Overview
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease in which the body either produces inadequate insulin or is unable to use the insulin that it does make, resulting in excessive blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Hyperglycemia, also known as high blood glucose or elevated blood sugar, is a common complication of untreated diabetes that causes catastrophic damage to many of the body’s systems, particularly the neurons and blood vessels.
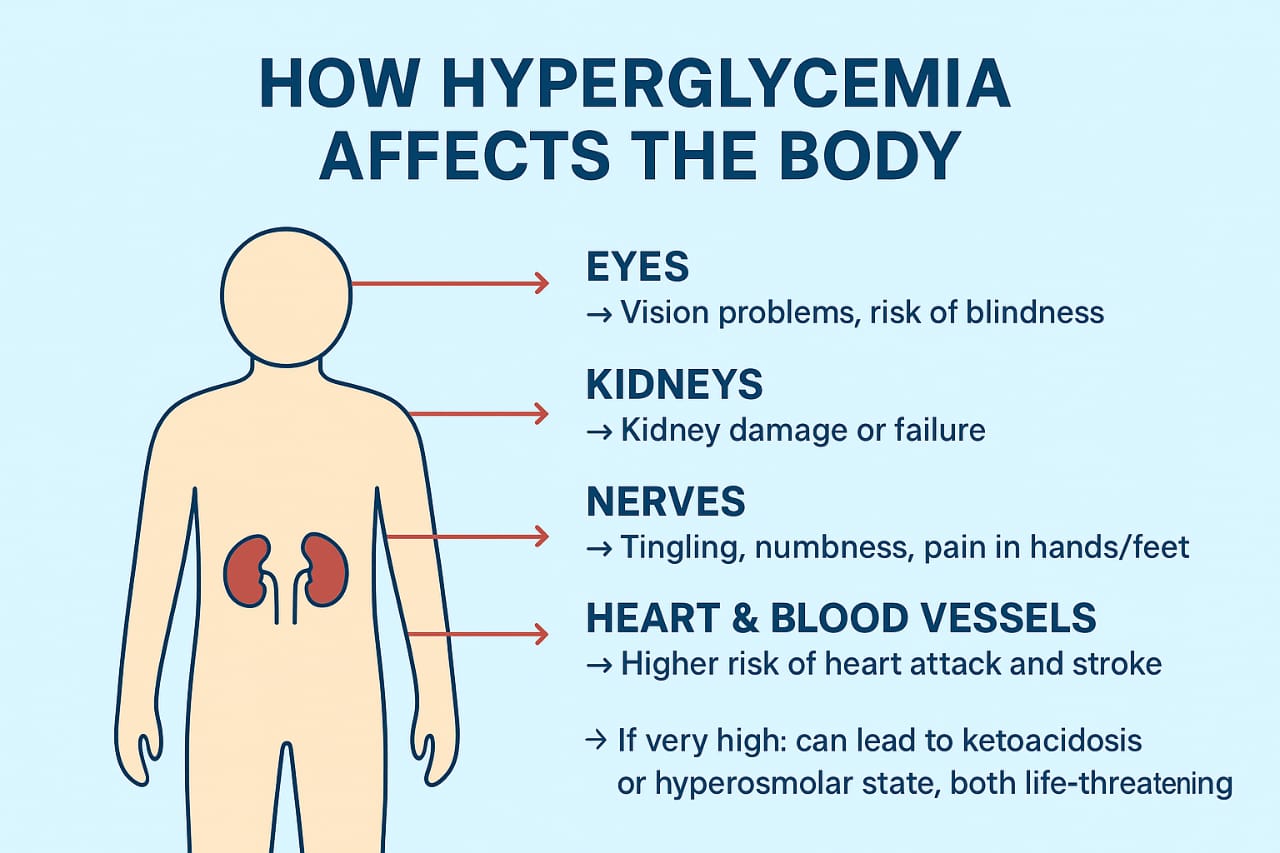
How Hyperglycemia Affects the Body?
When blood sugar stays too high for too long, it gradually harms multiple systems in the body:
- Nervous system: Damages nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain (diabetic neuropathy).
- Cardiovascular system: Injuries to blood vessels raise the risk of heart disease, stroke, and poor circulation.
- Kidneys: Overworks the kidneys, eventually causing diabetic kidney disease or failure.
- Eyes: Weakens tiny blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems and even blindness.
- Immune system: Slows healing and increases vulnerability to infections.
What are the types of diabetes?
There are three forms of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy).
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune disease, usually starting in childhood or young adulthood, in which the body makes little or no insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes: A metabolic disorder, mostly in adults, caused by insulin resistance and resulting in high blood sugar.
Gestational Diabetes: A temporary condition during pregnancy, marked by high blood sugar, which usually resolves after childbirth.
What are the causes of Diabetes?
- Genetic factors
- Obesity
- Unhealthy diet
- Hormonal disorders
- Sedentary lifestyle
By creating a diet plan for diabetes, we can
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Improve blood glucose levels.
- Reduce risk complications
- Decrease medicine requirements.
Indian foods for Diabetes Control
Green leafy vegetables: They are excellent for people with diabetes. The lower content of carbohydrates in green vegetables prevents a sudden rise in blood sugar levels. It also has lower calorie content. Green leafy vegetables contain essential minerals, phytochemicals, dietary fiber, and vitamins, all of which reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Garlic: It is one of the most frequently used foods in our kitchen. Garlic contains an active compound, allicin, which enhances insulin sensitivity and improves glucose metabolism, leading to better blood sugar control.
Cinnamon (Dalchini): It isn’t just a flavorful spice—it can also support better blood sugar control. Instead of making the body release more insulin, cinnamon helps your cells use insulin more effectively, which keeps blood sugar levels steadier. On top of that, its natural antioxidants protect your body from damage, lowering the risk of diabetes over time. A simple sprinkle in your tea, coffee, or oatmeal can be a tasty step toward better health.
Fatty Fish: Fishes like salmon, sardines, herring, and mackerel are excellent choices for people with diabetes. They are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Fatty fish are a good source of protein, which can promote feelings of fullness and potentially aid in weight management, an important factor in diabetes control.
Milk: It contains a healthy balance of carbohydrates and proteins that can help keep blood sugar levels stable. People with diabetes can benefit from adding milk and other dairy products—such as cottage cheese, buttermilk, and curd—into their meals. Whenever possible, it’s best to choose low-fat or reduced-fat dairy options to support overall health and blood sugar control.
Fenugreek Seeds (Methi Seeds): They are especially helpful for people with diabetes. They contain fiber and natural compounds that can slow digestion and reduce the body’s absorption of carbohydrates and sugar, which supports better blood sugar control. Research suggests that including fenugreek seeds regularly in the diet may be beneficial in managing type 2 diabetes.
Whole grains: Diabetes patients should include whole grains in their daily diet instead of refined flour. Chapati provides fibre, brown rice offers vitamins and minerals, quinoa is high in protein, and millets are gluten-free and rich in nutrients.
Moringa (Drumstick leaves): High in vitamin C, as well as calcium and iron. They help lower blood sugar and improve how your body uses insulin. Moringa is also good for our hearts.
How to use: Add moringa leaves to dals, soups, or dishes like kootu, poriyal, and sambar.
Pulses and Legumes
Pulses are high in plant-based protein and fiber, which help regulate blood sugar.
- Moong Dal: Easy to digest and low in GI.
- Chana (Chickpeas): High in protein and fiber.
- Rajma (Kidney Beans): Slow-digesting carbohydrates keep you full for longer.
- Urad Dal (Black Gram): It is beneficial for maintaining glucose levels.
Tips—Soak pulses before cooking to aid digestion.
Fruits
For individuals with diabetes, fruits like berries (strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries), apples, citrus fruits (oranges and grapes), pears, and kiwis are generally good choices. These fruits are typically low in glycemic index, meaning they don’t cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, and they offer valuable nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants.
- Berries: Strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries are excellent choices due to their low GI and high fiber content.
- Apples: Apples are a good source of fiber and can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Citrus Fruits: Oranges, grapefruits, and lemons are rich in vitamin C and fiber and generally have a low GI.
- Kiwis: Kiwis are packed with vitamin C and fiber and have a low GI.
- Cherries: Cherries, especially tart cherries, are a good source of antioxidants and have a low GI.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is glycemic index?
The glycemic index is a ranking system that measures how quickly a food raises your blood sugar levels after eating it.
What food should diabetic patients avoid?
Certain foods that can cause further increase in the blood sugar levels of diabetic people are sugar and its variants, deep-fried food, refined and processed food, canned food, and packaged snacks.
How often should I eat if I have Diabetes?
For people with diabetes, when you eat is just as important as what you eat. Instead of having large meals, it’s better to spread your food throughout the day.
How is diabetes diagnosed?
By conducting Urine tests, blood tests, and screening.
Can people with diabetes eat fruits?
Yes, fruit can be a part of a healthy diet for people with diabetes, as long as it is included in a balanced meal plan.
References:
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000305.htm
- https://www.who.int/health-topics/diabetes
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-2037144
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0753332223015329
- https://www.healthline.com/type-2-diabetes/what-to-eat
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes